Visual your problem more clearly. Help your doctor to provide more accurate treatment.
CBCT scans capturing data using a cone-shaped X-ray beam. CBCT is used in dental profession. These data are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional (3D) image of the following regions of the patient’s anatomy: dental (teeth); oral and maxillofacial region (mouth, jaw, and neck); and ears, nose, and throat (“ENT”). Also, the CBCT data can create 3D volumetric rendering.
What’s the difference between dental CT (CBCT) and medical CT?
- CBCT is better than the conventional CT used in medical field because it is less expensive and has lower doses of absorption.
- The CBCT systems used by dental professionals rotate around the patient, capturing data using a cone-shaped X-ray beam.
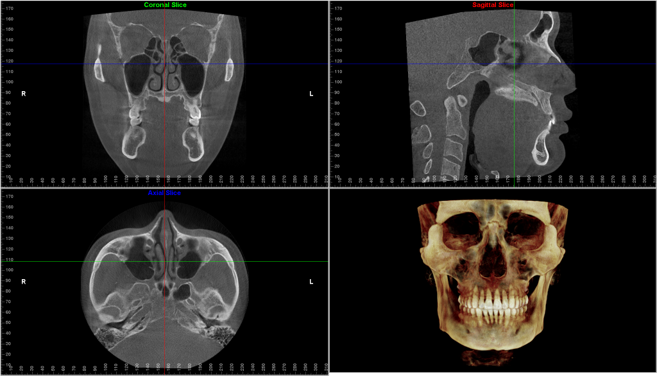
What’s the benefits of CBCT?
- dental CBCT, provides a fast, non-invasive way of answering a number of clinical questions.
- Dental CBCT images provide three-dimensional (3-D) information, rather than the two-dimensional (2-D) information provided by a conventional X-ray image.
- 2D imaging had some weakness such as image enlargement, elongated or shortened object, image distortion, superimposed structures. The real anatomy could be evaluate and analyzed better from three-dimensional (3D) image.
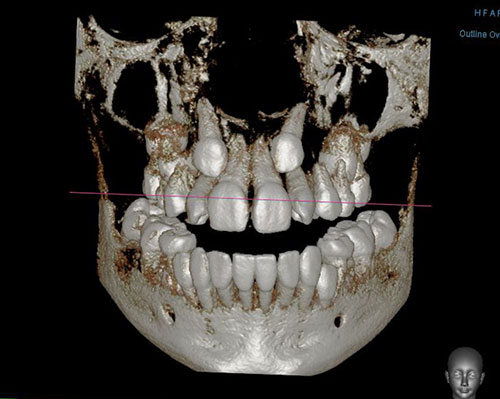
What’s the advantage of CBCT over 2D image?
- reliable diagnosis tool for the detection and quantification of bone resorption in periodontal diseases.
- Images without magnification
- Better visualization of the defective
- No distortion and overlapping of the images from CBCT.
CBCT presents better detail about the location of impacted or retained teeth or third molar, root resorption and cleft lip and palate except alteration of TMJ than panoramic radiographic.