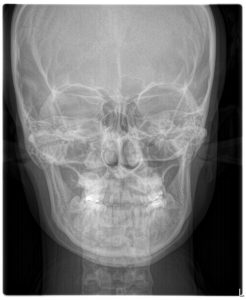
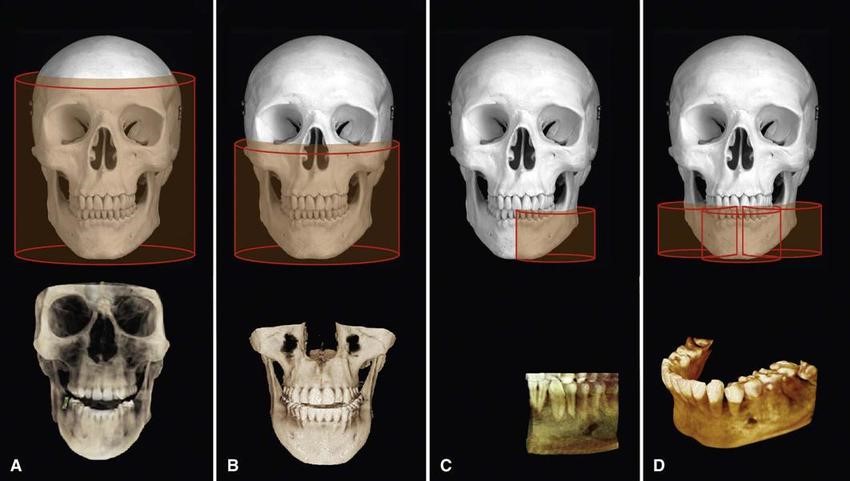
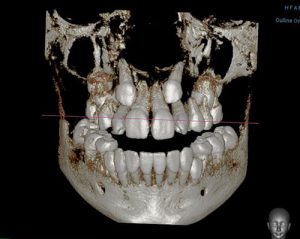
CBCT scan (3D x-ray)
Visual your problem more clearly. Help your doctor to provide more accurate treatment.
CBCT scans capturing data using a cone-shaped X-ray beam. CBCT is used in dental profession. These data are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional (3D) image of the following regions of the patient’s anatomy: dental (teeth); oral and maxillofacial region (mouth, jaw, and neck); and ears, nose, and throat (“ENT”). Also, the CBCT data can create 3D volumetric rendering.
What is the difference between dental CT (CBCT) and medical CT?
- CBCT is better than the conventional CT used in medical field because it is less expensive and has lower doses of absorption.
- The CBCT systems used by dental professionals rotate around the patient, capturing data using a cone-shaped X-ray beam.
What is the benefits of CBCT?
- dental CBCT, provides a fast, non-invasive way of answering several clinical questions.
- Dental CBCT images provide three-dimensional (3-D) information, rather than the two-dimensional (2-D) information provided by a conventional X-ray image.
- 2D imaging had some weakness such as image enlargement, elongated or shortened object, image distortion, superimposed structures. The real anatomy could be evaluated and analyzed better from three-dimensional (3D) image.
What is the advantage of CBCT over 2D image?
- reliable diagnosis tool for the detection and quantification of bone resorption in periodontal diseases.
- Images without magnification
- Better visualization of the defective
- No distortion and overlapping of the images from CBCT.
Due to present better detail, CBCT is used in many ways.
- Locate the impacted or retained teeth.
- Locate impacted tooth in order to place bracket for orthodontic treatment.
- Treatment planning for dental implant
- Surgical simulation for orthognathic surgery case (Surgery)
- Find the amount of root canals.
- Evaluate the bone height and thickness.
Digital X- Ray
A digital x-ray allows the dentist to take an image of the tooth or teeth and put it into an imaging program immediately. Within this imaging program, there are several tools that will allow the dentist to take a close look at the teeth and surrounding structures with amazing accuracy. As a benefit to the patient, the digital x-ray also provides nearly 80% less radiation than a standard x-ray. This is because the digital version of the x-ray is much more sensitive to this radiation and has been specifically designed with the patient in mind.
Procedure of digital dental X-ray
The actual procedure for having a digital dental x-ray is very similar to a traditional x-ray. our highly trained dental team will carefully insert a sensor into your mouth, and which will capture the image of your teeth or jaws. This digital sensor sends the information directly to a computer so that the images taken can be instantly viewed on a screen in the treatment room. Alternatively, images may be taken using a specialized scanner, or we can use a combination of a sensor and a scanner to produce a digital image. The exact method used is dependent on the type of x-ray required.
The benefit of Digital X-rays
- Once the digital image is on-screen, we can adjust it if necessary, enlarging or magnifying any areas which require close inspection. This makes it much more straightforward to identify any small cavities or other areas of concern.
- Diagnose any problems more efficiently and more quickly,
- Be available for viewing immediately since it does not have to be first developed like the old film x-rays.
- It is also very straightforward for us to show you these images on-screen and to explain any problems and how best to treat them.
- If a second opinion is required, these digital images can be emailed to a dental specialist, a process which is much faster and more efficient than having to mail conventional x-ray films.
- Available for patient education
What Are the Different Types of Digital Dental X-Rays?
Digital dental x-rays can be taken inside your mouth (intraoral), or they may be taken outside your mouth (extraoral).
Intraoral x-rays include:
- Bite-wing X-Rays: You must bite down on a sensor for an x-ray can be taken in a specific part of the mouth. Bite-wing x-rays are frequently used for detecting decay in between teeth, to check the condition of bone around teeth and to assess the fit and integrity of dental restorations including crowns and fillings.
- Periapical X-Rays: A periapical x-ray shows the entire tooth from its crown to the tip of the tooth root, as well as the bone surrounding the tooth. Periapical x-rays are useful in detecting periapical lesion and for assessing bone loss around the tooth which can occur if you have advanced gum disease.
Extraoral x-rays include:
- Panoramic X-Rays: A panoramic x-ray is taken by a machine that rotates around your head, providing a single detailed image of all your teeth in your upper and lower arch. Panoramic x-rays are particularly useful for assessing impacted wisdom teeth and other jaw problems, and for planning dental treatments including implants.
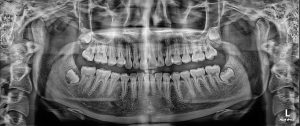
- Lateral Cephalometric x-rays: is particularly useful for orthodontic treatment planning.
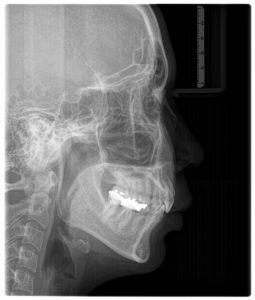
- Postero-Anterior Cephalometric x-rays is particularly useful for identify facial asymmetry in orthognathic surgery case.